Difference Between Colocation & Data Centers
Difference Between Colocation & Data Centers
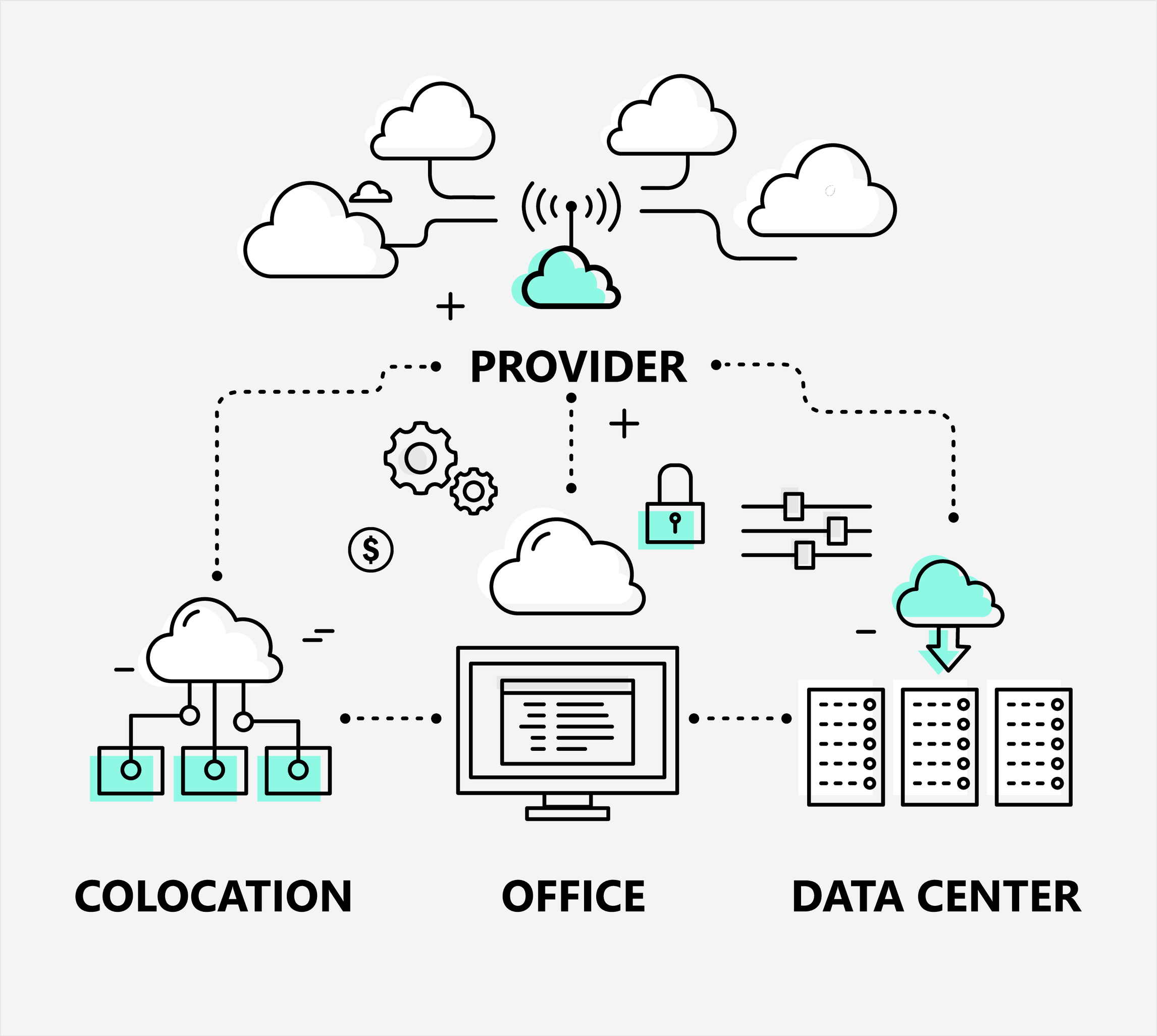
“What type of data center solution is best for me?” This is a common question that many people ask, and for good reason: we need to understand how our data is handled to plan for management and growth. There are various ways to set up your IT infrastructure, but choosing the best option requires planning and forethought about current and future data usage along with company goals. Two common IT infrastructure setups include ‘standard’ data centers and colocation data centers. While sometimes used interchangeably, the biggest differentiators are the level of ownership and required management of server security and upkeep.
What Is Colocation?
Colocation brings different servers owned by several companies that are operated and sometimes managed by a single but separate facility. It’s a popular method that allows a business to have a working data center without the costs associated with a new data center construction. The resources and management of the server(s) located in the colocation are sometimes provided by the IT staff on-site, usually for a contracted fee and time period.
For companies with a larger geographic service area, it’s not uncommon for one company to house multiple servers across different colocations. Colocations are usually, but not always, chosen due to their proximity to the business’s offices.
To make it easier to remember, colocation is a service offered by a data center, while a data center itself is the place where colocation is provided.
Benefits of Colocation
Think of colocation like renting an apartment versus homeownership. The colocation is the apartment, and your server(s) are the tenants. Renting the space and signing a lease guarantees a livable space for a predetermined amount of time. As opposed to homeownership (owning a data center), all or most of the maintenance and management typically required of servers is handled for you. Colocations offer excellent scalability at much lower costs than new construction.
Typically Lower Costs
Colocations tend to be cheaper since businesses are essentially renting space. Additional services may be added to a rental, such as on-site maintenance or the handling of hardware changes. Furthermore, the costs of the physical construction of a data center are eliminated, saving businesses even more money. Colocations also allow firms to avoid electricity, cooling, and security costs like fire, flood, and theft protection.
Less Labor Intensive
Because the core of the infrastructure in colocation is already available, your staff won’t need to perform laborious tasks like cable running or power management. Often, colocations offer hands-on maintenance, though this is an optional service.
Greater Reliability and Uptime
Similar to the benefits of lower costs, using a colocation avoids the need to have redundancy systems, power backup solutions, and ISP and telco vendors.
Mostly Fixed Costs
With some exceptions like paying for hardware changes or repairs, the monthly recurring costs of colocation utilization are highly predictable. This allows businesses to better budget for other priority areas like research and development or marketing.
Better Security
Most colocations are constructed to meet or exceed industry standards, including security measures. This provides physical security benefits of being in an occupied space along with cyber security benefits since colocations typically have state of the art firewalls, DDoS protection, and more.
What Is a Data Center?
A data center is a building that’s sole purpose is to house IT hardware like servers. An on-premises data center could be your servers in a closet or room that handles all your IT needs and requires considerable upkeep and day-to-day management. If you utilize colocation or cloud computing solutions, both scenarios have your data in a data center. The difference is: when you’re using colocation, you own the servers but not the data center; with cloud computing, you lease the servers from the data center.
Which Data Center Solution is Right for Me?
This all depends on your current needs and ultimate goals. For most purposes, cloud computing and colocation are typically the most economical options for most small to medium businesses. For enterprise customers, these may still be viable options, although again, that depends on the company’s size.
A company like Google owns its own massive, globally distributed network of data centers and offers data services like cloud computing as a product to other businesses. But a small app developer or SaaS company would likely benefit from the much lower costs of colocation or cloud computing services.
Scaling Your Business
Businesses usually have the goal of sustainable growth. Part of that growth comes at an expense, and for many companies, the highest costs are labor and IT. Contact us today if your company is looking to scale but unsure which data center option best suits your needs. We’ll help your business develop a sound strategy that places scalability and affordability as a priority.

